HTML Elements
script with defer & async attribute
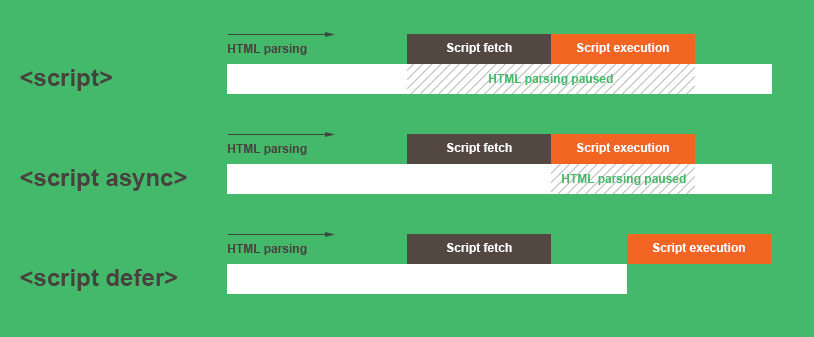
Plain <script>
For normal <script> tags without any async or defer, when they are encountered, HTML parsing is blocked, the script is fetched and executed immediately. HTML parsing resumes after the script is executed.
<script async>
In <script async>, the script will be fetched in parallel to HTML parsing and executed as soon as it is available (potentially before HTML parsing completes) and it will not necessarily be executed in the order in which it appears in the HTML document. Use async when the script is not critical to the initial rendering and doesn't depend/ is depended on other scripts, e.g. analytics.
<script defer>
In <script defer>, the script will be fetched in parallel to HTML parsing and executed when the document has been fully parsed, but before firing DOMContentLoaded. If there are multiple of them, each deferred script is executed in the order they appeared in the HTML document.
Use defer when the script relies on a fully-parsed DOM, as it can ensure that the HTML is fully parsed before executing. Or when the script depends/ is depended on other scripts, as the order of execution is guaranteed.
<table>
<table>
<caption>
Monthly savings
</caption>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Month</th>
<th>Savings</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>January</td>
<td>$100</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>February</td>
<td>$80</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
<tfoot>
<tr>
<td>Sum</td>
<td>$180</td>
</tr>
</tfoot>
</table>
<head>
<!DOCTYPE html>: HTML5, HTML cũ hơn thì dài hơn rất nhiều
<html lang="en" dir="rtl">
<head>
Set character encoding for the document
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
Viewport for responsive web design
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
Allows control over where resources are loaded from. Place as early as possible,
as the tag only applies to resources that are declared after it.
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
Control the behavior of search engine crawling and indexing
<meta name="robots" content="noindex,nofollow">
<meta name="googlebot" content="index,follow">
-------------------------------------------
<meta name="google" content="nositelinkssearchbox">
<meta name="google" content="notranslate">
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/products/phone" />
Name of web application (only should be used if the website is used as an app)
<meta name="application-name" content="Application Name" />
<link> ... Links to external CSS & JS files </script>
</head>
</html>
<meta name="robots
noindex: To not show this page in search results. Omittingnoindexwill indicate the page can be indexed and shown in search results. In a website, u might not want to index certain pages. Common use cases include settings pages, internal search pages, policies, and more.nofollow: To not follow links on this page. Omitting this will allow robots to crawl and follow links on this page. Links found on other pages may enable crawling, so if linkAappears in pagesXandY, andXhas a nofollow robots tag, butYdoesn't, Google may decide to crawl the link.
<meta name="googlebot"
Use this tag if you want to have a separate rule for Googlebot, and a general one for the rest of the search bots.
<link rel="canonical"
Content của example.com/products/phone trùng với example.com/phone → Chọn link này để Google ko crawl trùng.
Semantic
section(A group of content, typically with a heading), header, nav, main, footer, aside, article, address, figure.